This article explains how you can perform a traceroute on your Mac. You may use traceroute to diagnose network routing issues (e.g., connectivity problems) and other related problems because it is a a network diagnostic tool.
Print the route that packets take to a network host. Syntax traceroute options host packetsize Options host Host name or IP number -a Turn on AS# lookups for each hop encountered.-A asserver Turn on AS# lookups and use the given server instead of the default.d Enable socket level debugging.D When an ICMP response to our probe datagram is received, print the differences. To perform a traceroute on a Mac OS Xcomputer, you must open a Terminal window. The terminal can be found by opening the Finder, selection Applications and Utilities. To open a terminal session, double-click on 'Terminal.app'. Inside the Terminal application, the traceroute command is 'traceroute' and the specified target (i.e.google.com). Analyze your Internet connectivity with this program that combines Traceroute, Ping, and Whois tools in an intuitive graphical interface. Free to try Visualware Mac OS X 10.3/10.3.9/10.4 Intel. Free 30-day trial versions of VisualRoute for Mac OS X may be downloaded from the Visualware Web site. Pricing ranges from US $40 (for a single user) to $3,000 (for a 250 user license).
There are two ways to do this:
- Via the Terminal app
- Via the Network Utility app
See also: macOS Won’t Go To Sleep? Fix
To run traceroute on a Mac using the Terminal app
1-Launch the Terminal app. To open the Terminal app, you can:
- Go to Finder > Applications > Utilities > Terminal. Or alternatively,
- You may open it using Spotlight, open spotlight and search Terminal.
2-Type the following command and press Enter
traceroute hostname
In this command, hostname is the name of the server connection you are testing, like macreports.com. This could be a domain name or an IP address. For example, if we want to find the traceroute result for macreports, here is the command you need to enter:
traceroute macreports.com
As you can see above, you do not need to enter the “https://” or “www.” section of the website’s address.
3-It may take up to a few minutes for your Mac to complete the process. Your Mac will generate a list of connections between your computer and its destination.
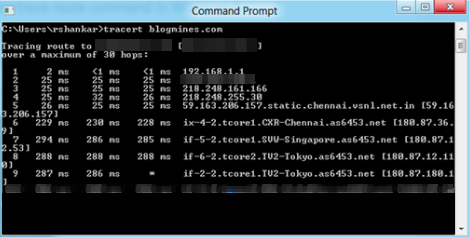
If you see * signs, that means “Request Timed Out”. Just wait. Then you may review the results.
See also: Where Do Screenshots Go On Mac?
To run traceroute on a Mac using the Network Utility app
You may also use the Network Utility app. Here is how:
1-Open the Network Utility app
- You can find Network Utility in /System/Library/CoreServices/Applications. Or alternatively:
- You can use Spotlight to open it.
2-Click the Traceroute tab.
3-Your your domain or IP number, like macreports.com and click Trace.
4-And review the results.
See also: How To Exit Safe Mode If Stuck

Print the route that packets take to a network host.
This program attempts to trace the route an IP packet would follow to some internet host by launching UDP probe packets with a small ttl (time to live) then listening for an ICMP 'time exceeded' reply from a gateway.
We start our probes with a ttl of one and increase by one until we get an ICMP 'port unreachable' (which means we got to 'host') or hit a max (which defaults to 30 hops & can be changed with the -m flag). Three probes (changed with -q flag) are sent at each ttl setting and a line is printed showing the ttl, address of the gateway and round trip time of each probe. If the probe answers come from different gateways, the address of each responding system will be printed. If there is no response within a 3 sec. timeout interval (changed with the -w flag), a '*' is printed for that probe.
We don't want the destination host to process the UDP probe packets so the destination port is set to an unlikely value (if some clod on the destination is using that value, it can be changed with the -p flag).
Notice that there are 12 'gateways' (13 is the final destination) and exactly the last half of them are 'missing'. What's really happening is
that rip (a Sun-3 running Sun OS3.5) is using the ttl from our arriving datagram as the ttl in its ICMP reply.
So, the reply will time out on the return path (with no notice sent to anyone since ICMP's aren't sent for ICMP's) until we probe with a ttl that's at least twice the path length. I.e., rip is really only 7 hops away. A reply that returns with a ttl of 1 is a clue this problem exists.
Traceroute prints a '!' after the time if the ttl is <= 1. Since vendors ship a lot of obsolete (DEC's Ultrix, Sun 3.x) or non-standard (HPUX) software, expect to see this problem frequently and/or take care picking the target host of your probes.
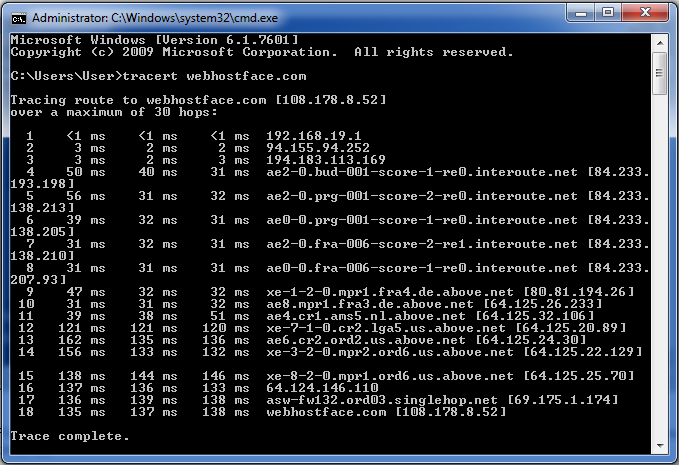
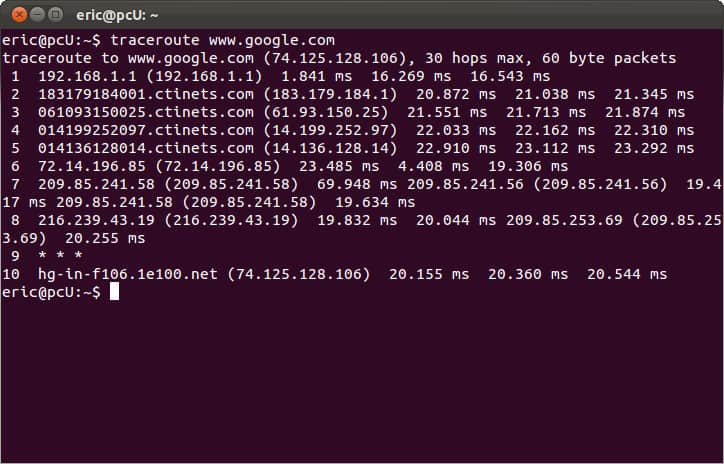
Other possible annotations after the time are !H, !N, !P (got a host, network or protocol unreachable, respectively), !S or !F (source route failed or fragmentation needed - neither of these should ever occur and the associated gateway is busted if you see one). If almost all the probes result in some kind of unreachable, traceroute will give up and exit.
This program is intended for use in network testing, measurement and management. It should be used primarily for manual fault isolation.
Because of the load it could impose on the network, it is unwise to use traceroute during normal operations or from automated scripts.
“The Net interprets censorship as damage and routes around it” ~ John Gilmore
Related macOS commands:
Traceroute Mac Terminal
netstat - Show network status.
ping - Test a network connection.
traceroute6 - Trace IPv6 Route to Host
Traceroute Mac Os X Terminal
Some rights reserved
